Table of contents
Today, lithium-ion batteries can be found in countless electrical appliances and machinery, including industrial trucks such as electric forklifts or pallet trucks. All lithium-ion batteries have one thing in common: these powerful energy storage units need regular charging.
So, how do you charge a lithium-ion battery correctly? Regardless of whether you use the Li-ion battery to power an industrial truck or a mobile phone, using the right charging method is important to ensure the longest possible battery life. In our guide, you can read about how to charge lithium-ion batteries, what to look out for during the charging process, what to avoid, the best way to maintain lithium-ion batteries, and how to proceed so that your device is optimally charged and ready for operation.
Lithium-ion battery charging tips
To prolong service life and avoid damage to the lithium-ion battery, you should consider the following charging tips for the best way to maintain lithium-ion batteries:
- Charge overnight if possible
 While it used to be said that you should never leave a battery charging unattended overnight, nowadays you can do this without any problems. For example, you can charge a battery installed in an industrial truck overnight, just as you can charge your smartphone beside you as you sleep.
While it used to be said that you should never leave a battery charging unattended overnight, nowadays you can do this without any problems. For example, you can charge a battery installed in an industrial truck overnight, just as you can charge your smartphone beside you as you sleep.
Lithium-ion batteries from Jungheinrich PROFISHOP are designed to be charged overnight without negatively impacting battery life in any way. Charging a lithium-ion battery sporadically throughout the day is also possible and the storage capacity will not be affected. - Don’t worry about overcharging
 Modern Li-ion batteries in electric pallet trucks have a built-in battery management system that, among other things, ensures for correct and effective charging – meaning it’s not possible to overcharge the battery.
Modern Li-ion batteries in electric pallet trucks have a built-in battery management system that, among other things, ensures for correct and effective charging – meaning it’s not possible to overcharge the battery. - Don’t let the lithium-ion battery drain completely
 Where possible, try to avoid a deep discharge of the battery, i.e., avoid letting the lithium-ion battery drain completely. If you use a lithium-ion battery until it is completely discharged, the voltage of the battery drops below the end-of-discharge voltage which can damage the battery in the long run.
Where possible, try to avoid a deep discharge of the battery, i.e., avoid letting the lithium-ion battery drain completely. If you use a lithium-ion battery until it is completely discharged, the voltage of the battery drops below the end-of-discharge voltage which can damage the battery in the long run.
This voltage level is 2.5 volts for lithium-ion batteries and 3.3 volts for lithium-polymer batteries. Reasons for a deep discharge can be defective chargers, a faulty automatic cut-off and, in vehicles, a short circuit or a defective alternator.
Pallet trucks or stacker trucks with lithium-ion batteries are not affected by deep discharge due to their integrated safety system. - Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures
 Lithium-ion batteries are very sensitive to temperature. As a result, devices equipped with these kinds of batteries should not be exposed to temperatures above 40˚C or below -10˚C, nor should they be charged at these temperatures.
Lithium-ion batteries are very sensitive to temperature. As a result, devices equipped with these kinds of batteries should not be exposed to temperatures above 40˚C or below -10˚C, nor should they be charged at these temperatures. - Never store the battery empty
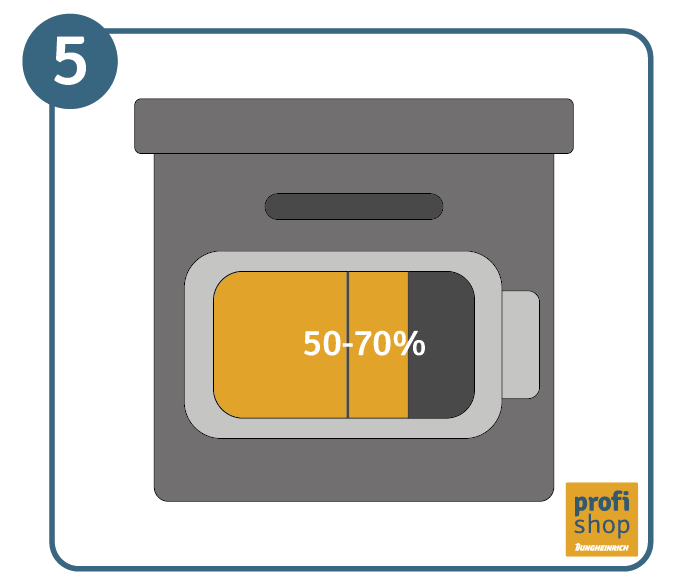 The best way to maintain lithium-ion batteries during storage is by first charging them at up to 50 to 70 percent of their capacity. Optimal storage temperatures are 15 to 18˚C. At this temperature the batteries remain efficient, and the risk of deep discharge is reduced – even during longer periods of storage. Special hazardous material cabinets are a safe choice when it comes to storing lithium-ion batteries, however, they are not necessary for the charging process.
The best way to maintain lithium-ion batteries during storage is by first charging them at up to 50 to 70 percent of their capacity. Optimal storage temperatures are 15 to 18˚C. At this temperature the batteries remain efficient, and the risk of deep discharge is reduced – even during longer periods of storage. Special hazardous material cabinets are a safe choice when it comes to storing lithium-ion batteries, however, they are not necessary for the charging process.
Memory effect in lithium-ion batteries: does it exist or not?
The so-called memory effect in lithium-ion batteries, especially in the past, may have a negative impact on the storage capacity of batteries. The memory effect is triggered by the frequent partial discharging of the battery. This creates a premature voltage drop, causing the cell voltage to fall below the minimum requirement of the unit. Subsequently, the accumulator stores the charge level of the partial discharge as a “memory” and only provides a reduced capacity. Further partial discharges increase the effect.
Despite sufficient charge, the performance of the battery decreases. The device using the battery no longer functions for the usual length of time and the battery must be recharged much more frequently. If the lithium-ion battery memory effect is pronounced, the unit can even become unusable long before the end of its service life.
Modern rechargeable lithium-ion batteries do not have a significant memory effect. This was more likely to have been the case with nickel-cadmium batteries or nickel-metal hybrid batteries used in the past. Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute in Switzerland and at Toyota’s research laboratory in Japan were able to observe the effect in lithium iron phosphate (LiFePo) batteries. However, during their testing the researchers found that the voltage change is temporary and only in the per mille range. They also found that it can be reversed with a waiting period between partial charging and complete discharging.
How do you charge a lithium-ion battery? Even if a lithium-ion battery has some power, it can still be temporarily charged at any time. Intermediate lithium-ion battery charging can also partially be carried out at any time. For example, you can charge a vehicle powered by a lithium-ion battery, such as an electric stacker truck, during a work break. Above all, it’s important to make sure that you switch off the charger before disconnecting the battery from the device.
If you frequently need to charge a lithium-ion battery, you should aim to charge it at regular intervals of approx. 4 weeks or so. This will ensure that the battery works reliably. You should also make sure to charge the battery fully before using it for the first time.
Charging lithium-ion batteries: FAQ
The memory effect is a loss of storage capacity caused by charging the battery too early. A memory effect can occur with previously used nickel-cadmium batteries or nickel-metal hybrid batteries. Always discharge these batteries completely before recharging them. With modern lithium-ion batteries, there is no noticeable memory effect.
No. The construction and function of lithium-ion batteries used for operating industrial trucks prevents overcharging. These batteries have an integrated battery management system that guarantees an optimal charging process.
No. Discharging, or letting a lithium-ion batter drain completely is not necessary. You can recharge a Li-ion battery at any time without having to discharge it first. Flat charging cycles with a capacity between about 30 and 80 percent are best.
There can be various reasons why a lithium-ion battery no longer charges or no longer charges fully:
• the battery is defective
• the charger and battery are not connected properly
• the charger cable is defective
• the charger or charger cable is incompatible
• the battery is too old
• the ambient temperature is too high or too low
If your battery is no longer charging, check all possible causes. If it turns out that the battery is defective or outdated, it is usually not worth repairing. In this case, you will need to correctly dispose of the lithium-ion battery and replace it with a new one. The above advice also applies to lithium polymer battery charging.
How often you can charge a Li-ion battery depends on how you look after it. If you always charge the battery correctly, it can last up to 500-800 charging cycles. Lithium-polymer batteries, which have a higher energy density, have a slightly shorter lifespan of 300-500 charging cycles. A complete charging cycle corresponds to a charge of approximately 70 percent.
Image source:
© gettyimages.de – roman023