Table of contents
As global focus shifts towards sustainable building practices, construction companies are turning to more eco-friendly materials for both public buildings and residential homes. Considered one of the most sought-after building materials, wood is a versatile material that can be used both indoors and outdoors, all while remaining resistant to weathering and wear. With good insulating qualities, wood and subsequently, wood wool, have both grown in popularity as building materials.
This not surprising, as wood wool can significantly improve the ecological balance of a building, providing improved insulation without compromising the quality or durability of the construction. It’s also renewable and sustainable, provided it’s sourced locally or from certified regions. In this guide, you’ll find everything you need to know about wood wool, including its composition, uses and advantages.
Production and applications of wood wool
So, what is wood wool? Wood wool essentially consists of wood fibres (typically from wood shavings or planks left over from other purposes) that have been processed into elastic threads via special machinery. During production, the wood must not contain more than 13% residual moisture, which is why it sometimes undergoes a special drying procedure to keep it from dampening. Both softwoods and hardwoods can be used, but each type gives different insulating properties to the end results.
Unlike wood chips, wood wool is almost entirely splinter-free. It can be used loose and by itself for various purposes, including waterproofing and as a filling material, or it can be combined with a binding agent (like cement) and pressed into boards. If you’re wondering what wood wool is used for around the house, here are some common uses of the material:
- Roof insulation as wood wool rolls
- Insulation boards for interior walls and ceilings
- Blown insulation for hollow building materials
- Waterproofing and natural weather protection
- Plaster boards for exteriors and façades
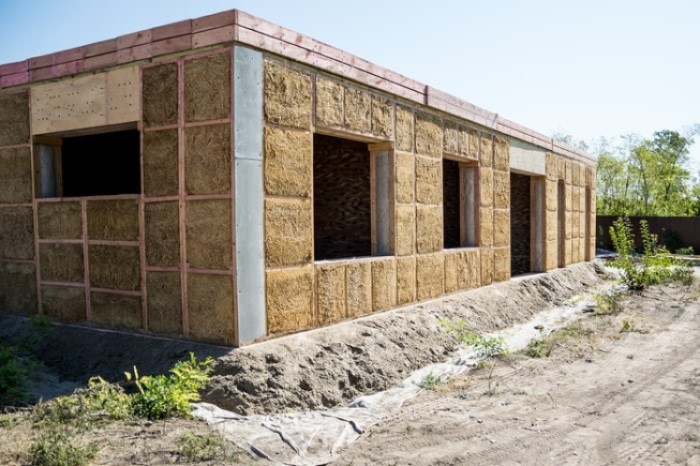
For exterior walls, wood wool is usually used as a composite material. This means that a separate insulating material is placed in between two insulation boards made of wood wool to improve both the heat retention and energy efficiency of the building.
How effective is wood wool as an insulator?
Wood has been used as a building material for centuries, since it’s naturally abundant, quickly renewable, and a very good insulator. Wood wool benefits from these properties too, which is why it’s ideal for insulating buildings during construction. Here are some other advantages of the material:
- Heat protection
 Wood wool has a high heat storage capacity, which ensures buildings in hot climates don’t warm up quickly. This material can provide much-needed protection from the summer heat, especially when used in roofing.
Wood wool has a high heat storage capacity, which ensures buildings in hot climates don’t warm up quickly. This material can provide much-needed protection from the summer heat, especially when used in roofing. - Insulation
 At 0.09 kelvin-metres per watt, the thermal conductivity of wood wool is well within the acceptable range for insulation materials. That said, it is quite high in comparison to other materials, which leads to greater energy losses in the winter months. This issue can be avoided by mixing or combining it with other insulating materials.
At 0.09 kelvin-metres per watt, the thermal conductivity of wood wool is well within the acceptable range for insulation materials. That said, it is quite high in comparison to other materials, which leads to greater energy losses in the winter months. This issue can be avoided by mixing or combining it with other insulating materials. - Fire protection
 Depending on the composition, wood wool panels can attain varying levels of fire protection. They can be classed as flame-retardant and non-combustible and offer comparatively better protection from fire than other insulation materials.
Depending on the composition, wood wool panels can attain varying levels of fire protection. They can be classed as flame-retardant and non-combustible and offer comparatively better protection from fire than other insulation materials. - Sound insulation
 The material is great at dampening noise, so it is ideal for soundproofing buildings in areas where noise pollution is a problem.
The material is great at dampening noise, so it is ideal for soundproofing buildings in areas where noise pollution is a problem. - Moisture level regulation
 Wood wool absorbs moisture well and provides a healthy indoor climate.
Wood wool absorbs moisture well and provides a healthy indoor climate. - Durability
 Wood and its various derivatives (like wood wool) are naturally protected against rot and disease, so they maintain good durability provided there is sufficient air flow.
Wood and its various derivatives (like wood wool) are naturally protected against rot and disease, so they maintain good durability provided there is sufficient air flow.
Considering the properties mentioned above, it’s clear why wood wool is a popular insulating material in construction. Take a look at the advantages and disadvantages of the material listed below:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| • High heat storage capacity for excellent heat protection • Efficient sound and noise protection • Good protection against fire • Natural humidity regulation • Resistant to rot, fungal infections and disease. • Very strong and dimensionally stable material | • High thermal conductivity and therefore reduced heat retention and insulation when used by itself • Good insulation is only achieved when used in thick amounts • Fairly expensive |
How much does wood wool cost to use as insulation?
The cost of wood wool is quite high in comparison to other insulating materials. In the UK, wood wool boards are around £10 to £25 per square metre, depending on the type of wood, the board thickness and the binding material used. These panels are often cheaper if cement is used instead of magnesite, for instance. You’ll also have to factor in installation costs, which can total around £50 per square metre.
When used in exterior insulation, the boards must be thicker to comply with certain thermal insulation regulations. This means that it can be even more expensive. However, costs can be kept down by using composite building materials like cellulose and mineral wool between wood wool panels. This gives better insulation and reduces overall costs.
Eco-friendly construction is actively promoted by the UK government. It’s always worth enquiring whether your building project is eligible for funding or grants, and to see which materials you need to include to receive them.
How sustainable is wood wool as an insulation material?
Wood wool is a very sustainable building material, as it is completely biodegradable, carbon-neutral and can be made from recycled and repurposed materials. What’s more, it requires no additional energy aside from that used in its processing. However, wood wool is only sustainable if you adhere to the following two conditions:
- Location and proximity: Keep your construction sustainable by using only wood wool from local sources and from native tree species.
- Ecology: Make sure your wood wool comes from sustainable forestry. You can identify this by looking for various badges attributed to sustainable practices.
Good to know: In addition to wood wool, there are other sustainable materials that you can use as building and insulation material. Increasingly popular ecological alternatives include straw — which has already been in use for centuries as an insulating material — and cork.
FAQs about wood wool
Because of its high heat storage capacity, wood wool cools buildings down during the warm summer months. However, its high thermal conductivity means it is not the best for retaining heat during the winter. To prevent energy loss during colder months, it is often combined with other materials to provide added insulation for exterior walls.
Wood wool is generally flame-retardant, which means it offers good protection against fires. Its effectiveness as a non-flammable building material depends on its grade and whether it is combined with other compounds.
Once it’s been installed, wood wool is completely harmless. However, during construction and production you should wear a respiratory mask and cover your skin as much as possible. The dust generated can cause irritation to the skin and breathing problems.
Image source:
©getty: Zbignev Safranovic